Dec 2, 2024
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) has surged to the forefront of technological innovation, reshaping the way we interact with digital content. With capabilities that range from generating text and images to creating voice replications and synthesizing video, generative AI holds immense potential across many industries. Tech giants like Apple and META have taken significant steps in this space, with Apple recently launching its AI tool, Apple Intelligence, and META continuing to expand its suite of AI-driven solutions. These advances highlight the widespread appeal and utility of generative AI in both consumer and enterprise contexts.
However, as generative AI tools become more integrated into daily life, concerns around data privacy and security are growing. Each interaction with these AI systems often involves sharing personal data, raising questions about how that information is collected, used, and protected. For companies, developers, and users alike, it’s essential to address whether generative AI tools are truly safe and what safeguards are in place to protect user privacy.
In this article, the cybersecurity experts at Blade Technologies explore the privacy and security implications of generative AI. By examining the unique challenges of generative AI, the privacy measures currently in place, and best practices for users, we aim to shed light on the future of secure, privacy-conscious AI tools in the digital world.
Understanding Generative AI
Generative AI is a branch of artificial intelligence that can create new content, whether it’s text, images, audio, or even video, by learning from large datasets. Unlike traditional AI, which focuses on pattern recognition and predictions, generative AI uses advanced models like neural networks to “generate” new data that mirrors the patterns, styles, or structures in the original datasets. These systems have opened doors to a variety of applications, from virtual assistants and chatbots to complex image and video generation tools that can produce hyper-realistic media.
Apple’s recent launch of Apple Intelligence showcases how generative AI can be embedded within products to enhance user experiences by providing relevant suggestions, organizing data, and creating content tailored to user needs. This tool reflects how generative AI is transforming consumer interactions and boosting both productivity and personalization in online interactions.
Privacy and Security Concerns in Generative AI Tools
As generative AI tools become more sophisticated, privacy and security concerns continue to mount. These tools often require extensive data for training, including potentially sensitive or personal information, making data protection a critical issue. In many cases, users may not fully understand what data is being collected, how long it is retained, or how it is ultimately used. This lack of transparency raises significant privacy concerns, especially when large volumes of data are stored and processed by companies for AI development and research.
Collection and Retention of Personal Data
To create accurate and relevant outputs, AI systems often rely on detailed user data, which can include personal preferences, browsing history, voice samples, and even image data. This data may be retained for extended periods, potentially making it vulnerable to unauthorized access or misuse. For instance, data breaches or internal leaks could expose private information, leading to identity theft, fraud, or other harmful outcomes for users.
Misuse of AI-Generated Content
There is also the potential for AI-generated content to be misused, particularly in the context of misinformation, deepfakes, and unauthorized use of personal likenesses. Generative AI can easily produce realistic but false content, such as manipulated images or fabricated text, which can mislead audiences or tarnish the reputations of individuals and companies alike. This is especially problematic when it comes to tools that replicate human voices or appearances, as they can be exploited to create fake audio or video that appears authentic.
User Authentication and Consent
User authentication and consent are also critical issues, especially when generative AI tools involve sensitive content or actions. For example, AI systems that generate voice or video outputs could, if mishandled, lead to unauthorized use of a person’s likeness or voice. Without clear policies and safeguards, these tools could inadvertently or intentionally be misused, raising ethical and legal questions about consent and privacy.
Privacy Safeguards Implemented by Major Players in AI
As privacy concerns remain at the forefront of AI usage, major technology companies like Apple and META are beginning to implement safeguards to protect user data. Each company has taken a unique approach, reflective of its broader stance on privacy and transparency, though the exact details of their strategies are often kept opaque.
- Apple Intelligence is a recent addition to Apple’s suite of AI-driven tools, reflecting the company’s longstanding commitment to innovation. Apple’s privacy approach is built around principles like data minimization and on-device processing. By processing data locally rather than in the cloud, Apple reduces the need to transfer or store personal data externally, minimizing potential exposure. In many cases, Apple’s tools are designed to function with only anonymized, aggregated data, ensuring individual users cannot be identified from AI-generated insights. Users can also adjust privacy settings, manage app permissions, and delete stored data whenever they choose.
- META has evolved its approach to privacy over recent years, influenced by its history with data privacy controversies and regulatory pressures. As META expands its AI capabilities, particularly in social media and augmented reality (AR), it has introduced more detailed privacy settings and controls for users to manage what data they share. However, unlike Apple, META’s business model relies heavily on user data to fuel targeted advertising, making it more challenging for META to embrace stringent data minimization practices. In response to increasing scrutiny, META has introduced transparency reports and consent management features, allowing users to better understand how their data is used and stored.
Practical Steps for Safeguarding Data in Generative AI
With generative AI tools becoming more widely adopted, both individuals and organizations need to be proactive in protecting their data. While companies like Apple and META have implemented privacy features, users must also take steps to ensure their own data security. Here are some practical steps and best practices that can help both individuals and enterprises maintain privacy and security when using generative AI.
User Best Practices
- Review Privacy Policies and Permissions: Before using generative AI tools, users should carefully read privacy policies and terms of service to understand what data the tool collects, how it is used, and who has access to it. Many AI applications request permissions to access personal information, so adjusting these permissions to the minimum necessary for functionality is an effective first step.
- Opt-Out Options and Data Deletion: Many AI tools provide options to opt out of data sharing or to request data deletion. Users should explore these features to ensure their data isn’t unnecessarily stored or used for secondary purposes, such as targeted advertising. META, for instance, has detailed settings for managing data preferences on its platforms, and Apple allows users to delete stored data from many of its services.
- Exercise Caution with Sensitive Data: Avoid sharing sensitive personal information with AI tools unless absolutely necessary. Many generative AI applications require access to photos, audio, or location data, which may be vulnerable if stored insecurely or retained for extended periods. Users should limit sharing this data whenever possible.
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): If an AI tool requires login or collects personally identifiable information (PII), MFA adds a layer of security, protecting accounts from unauthorized access. MFA is particularly important for users of cloud-based AI services, where a breach could expose large amounts of data.
Business Policies and Best Practices
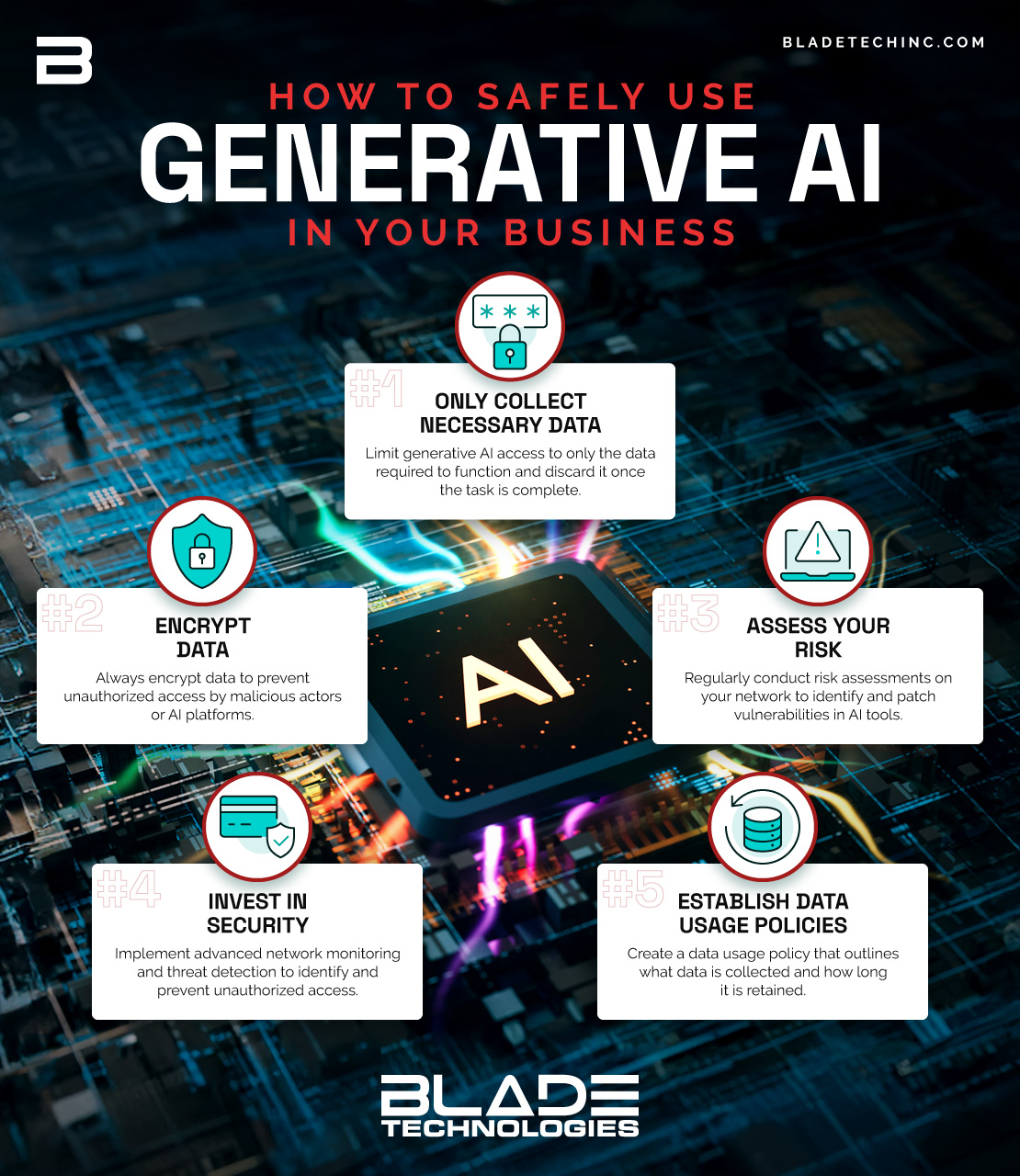
- Adopt a Data Minimization Strategy: Organizations implementing generative AI should follow data minimization principles, collecting only the data necessary for the tool’s function and discarding it once the task is complete. This reduces exposure risk if there is a breach and ensures compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR, which mandate strict data minimization.
- Secure Storage and Encryption: Storing data in secure environments and using encryption techniques for data at rest and in transit is essential to prevent unauthorized access. Businesses should consider using cloud providers that comply with industry security standards and offer end-to-end encryption.
- Regular Audits and Risk Assessments: Conducting regular audits and risk assessments can help identify potential vulnerabilities in generative AI tools and address them proactively. Organizations should also establish a protocol for monitoring the use of generative AI tools and updating security measures in response to new threats or changes in data privacy laws.
- Integrate with Third-Party Security Tools: Many cybersecurity firms, including Blade Technologies, provide tools and services that can enhance the security of generative AI systems. For example, deploying advanced network monitoring and threat detection can help monitor and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data within AI environments. Blade Technologies can also support compliance with regulatory standards, reducing legal and reputational risks.
- Implement Clear Data Usage and Retention Policies: Establishing transparent data usage policies helps ensure employees and clients understand what data is collected and how long it will be retained. This builds trust with customers and helps prevent misuse of data within the organization. These policies should also outline procedures for data deletion and anonymization to protect user privacy.
Protect Your Data with Blade Technologies
As generative AI becomes a part of everyday life, its potential benefits are matched by significant privacy and security challenges. Tools from industry leaders like OpenAI, Apple, and META have brought the capabilities of AI closer to consumers and businesses, yet questions remain about how user data is protected and how transparency can be improved. The key to safely navigating this landscape lies in understanding the privacy safeguards that are in place, practicing responsible data handling, and remaining vigilant about potential risks.
For users and organizations alike, safeguarding privacy with generative AI tools requires both awareness and action. Ongoing collaboration among users, organizations, and technology providers will be crucial to ensure a balance between innovation and privacy. If you or your business have questions about data privacy, generative AI, or cybersecurity best practices, Blade Technologies is here to help. Contact our experts today to discuss your privacy and security needs and let us help you build a secure foundation for using advanced AI tools.
Contact Us